Type 2 Diabetes Diet Plan – Symptoms, Prevention, Treatment for Men and Women
As seen from my clinical practice, a few people who are diagnosed to have Type 2 diabetes are symptomless and are noted without any specific complaints.
The classical signs and symptoms of Type 2 diabetes need not be present in all the patients.
Unlike Type 2 Diabetes vs Type 1, some people have common classical symptoms of diabetes which are easy to diagnose whereas some individuals have unusual and rare symptoms, which give a clue to suspicion of diabetes.
Diabetes is rapidly rising since the last few decades, and we all need to know the signs and symptoms of diabetes, which helps in the early detection and treatment of the same.
The COMMON signs and symptoms of diabetes are:
1. Increased thirst
2. Frequent urination
3. Increased hunger
4. Tiredness
5. Unexpected weight loss;
6. Blurring of vision
The UNUSUAL or LESS COMMON signs and symptoms of Diabetes are:
- Frequent infections:

Image Source – Dabur
Diabetes leads to low immune status. Low immune status leads to frequent infections.
Since Yeasts (fungus) and Bacteria multiply in high numbers in presence of sugars, frequent infections are common in diabetes.
- Slow healing wounds:
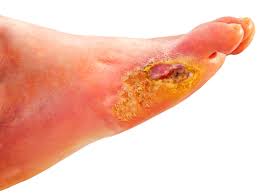
Image Source – YouTube
A high blood sugar level will decrease the amount of oxygen delivered to the wounds via the bloodstream, which hence slows down the overall healing process.
- Darkening of skin:
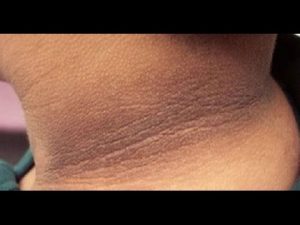
Image Source – Pinterest
Dark, velvety patches in the folds of skin, usually on the back of neck, knuckles, and elbows are often early warning signs of high blood sugar. High insulin levels increase melanin levels and make skin look dark.
- Improvements in vision:

Image Source – Endmyopia.org
High blood sugar in Diabetes causes the shift of fluid levels including the lenses of eyes, leading to a change of refractive power and change in power of glasses for better vision.
This sometimes leads to improvement in vision and no need for glasses. When blood sugars are controlled on treatment, again refractive errors of the lens goes back to previous levels and one needs glasses again.
- Tingling and numbness in limbs:
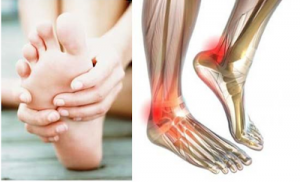
Image Source – Pinterest
A high blood sugar level may cause nerve damage, further eventually leading to tingling and numbness-like sensations in the limbs.
- Itching of skin:
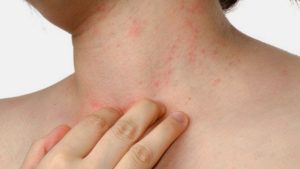
Image Source – Health Tap
Diabetes impairs blood circulation and can lead to dryness and itching.
- Decreased hearing:
Image Source – Click.in
Hearing loss could be an early sign of diabetes. Diabetes damages the blood vessels and nerves of the inner ear leading to decreased hearing.
- Increase in snoring :

Image Source – Homemade Health and Beauty Tips
One study confirmed 23% of sleep apnea which is characterized by loud snoring and daytime sleepiness will develop diabetes in the next 5 years.
People with disordered breathing, tend to release stress hormones during sleep which can lead to an increase in blood sugars.
- Sexual issues:

Image Source -Homemade Health and Beauty Tips
High blood sugar can cause damage to blood vessels and nerves that are needed for normal sexual response leading to sexual dysfunction in both men and women.
UNIQUE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF DIABETES IN MEN;
Apart from above common signs and symptoms, men can have
1. Erectile dysfunction
It is the inability of a man to achieve or maintain an erection. According to a recent meta-analysis of 140 studies, 50% of men with Type 2 Diabetes are suffering from erectile dysfunction.
2. Retrograde ejaculation;
Semen instead of ejected outside is being released back into the urinary bladder.
Thus very less semen gets released during sexual ejaculation.
3. Urological issues like hyperactive bladder, inability to control urine and urine infections.
Urological issues can happen due to diabetic nerve damage.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS UNIQUE TO WOMEN ARE:
1. Vaginal itching and fungal infections
2. Lower sexual drive and some cases lead to painful sex.
3. Frequent urine infections
The cause of the above 3 symptoms of diabetes in women has been explained above.
4. Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS).
Women with PCOS are at greater risk of diabetes. Symptoms of PCOS are irregular cycles, weight gain, and acne along with fertility problems.
PCOS leads to insulin resistance which in turn causes diabetes.
All diabetes people and their family members must have knowledge of the signs and symptoms of diabetes which helps in early detection of high blood sugar and its complications.
The Main Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
Even the researchers do not provide clear evidence of what causes diabetes exactly. However, there are a few factors that can be denoted as Type 2 Diabetes causes. They include genetic factors, lifestyle factors, hereditary factors, and more.
But at its bottom line, Type 2 diabetes is well-identified usually with the following two indicators. This is quoted from a source in line with the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK);
- Insulin Resistance – A high blood sugar level or clinically referred to as hyperglycemia is witnessed, when the hormone, insulin is not sufficiently utilized by the human body. Eventually, the body takes much higher levels of insulin than the optimal bar, to transport the blood sugar, i.e. glucose into the cells; for immediate usage as energy or even stored for any later purpose.
Again, NIDDK pinpoints out that insulin resistance makes diagnosis quite difficult as it does not highlight the Type 2 diabetes symptoms visibly outside.
- Prediabetes – The blood sugar level inside the body will hike up if the level/quantity of production of the insulin hormone is limited to the actual need. NIDDK states that prediabetes is a precursor to Type 2 diabetes itself.
Yet, prediabetes is not the worse part, because if the physician can diagnose the problem, then with some proper lifestyle alterations and diet changes, the issue can be effectively resolved.
These are some of the Type 2 Diabetes Risk Factors
When it comes to the Type 2 diabetes risk factors, the following key points denote the ones seen most frequently with people. And note that the problem itself is a multifactorial disease, and you cannot just cut down eating excess sugar or suddenly increasing your physical activity;
- Obesity:
As per the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), you must have a proper check of your BMI or Body Mass Index; as it puts you into being overweight or obese, which ultimately is a risk factor to acquire Type 2 diabetes.
- Poor Eating Habits:
It is proven that consuming more amounts of processed, high-calorie foods, will drastically improve your risk factor to get Type 2 diabetes. This is as per the American Diabetes Association (ADA). so, reduce your intake of coffee, cake, sodas, white bread, etc. and go with fresh fruits, green veggies, whole grains, water, and tea.
- Too Much TV Time:
Regarding the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, it is said that prolonged duration spent sitting in front of the television will increase the chances of getting Type 2 diabetes along with many other physical ailments as well.
- Not Getting Enough Exercise:
To protect one’s body from insulin resistance and even for Type 2 diabetes prevention, consider the notion of doing regular exercises. With good cardiovascular health and a fit muscle mass, your body will interact with all the hormones healthily.
- Sleep Habits:
The National Sleep Foundation states that the demand for the pancreas will increase if there is a loss of balance for insulin by the body, which is primarily affected by a few sleep disturbances.
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS):
PCOS, a hormone imbalance disorder, most common with today’s females, unfortunately, holds a higher risk for Type 2 diabetes than the rest, owing to the obesity and insulin resistance seen as common denominators with this health condition.
- Being Over Age 45:
As per the American Diabetes Association, being old itself is a risk factor for Type 2 diabetes. So, the older you grow, the more prone you are to acquire the disease. But in recent times, even teenagers and a few children are getting affected because of prediabetic conditions and Type 2 diabetes.
How is Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed?
It has been said that if you are older than 45 years or even if you are overweight, then it is advisable to take up a diabetes checkup every 3 years. Because only early detection and immediate treatment can help fight back this disease.
- Glycated Hemoglobin (A1C) Test – A1C is a test administered as a 2 to 3-month measurement of a person’s average blood sugar level. And these are the general reading values; 5.7 or below means normal, between 5.7 and 6.4 per cent means prediabetes and 6.5 per cent or higher in any of these two different tests denote that the person has diabetes.
- Fasting Glucose Test – More of a conventional test, it involves the person tested giving a sample of blood in a laboratory setup, after an 8 hours duration of fasting. The normal blood sugar level is represented if the ‘fasting blood sugar level’ is less than 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). But if the range falls between 100 to 125 mg/d, then it denotes prediabetes. And finally, diabetes is diagnosed if the test measures more than 126 mg/dL on any two separate occasions. These ranges are as per the diabetes guidelines of ADA.
The Span of Type 2 Diabetes
Before highlighting the point of duration, it is important to state here that only the symptoms of Type 2 diabetes can be managed and one cannot alter the underlying predisposition for insulin resistance.
And so, here are some methods by which anyone can reduce or manage their existing blood sugar levels:
- Diet changes.
- Lifestyle modifications.
- Injectable medications.
- Complementary therapies
- Inhibitors.
- Oral prescriptions.
- Alternative therapies.
- Insulin treatments.
Additionally, the individual should also get ready to lose around 5 to 7 per cent of his or her total body weight. With the data of CDC, the participants involved in the national Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) exercised for at least 150 minutes weekly and also reduced their weight greatly. As a result, they cut the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes by 58 per cent!
What’s the Type 2 Diabetes Diet Plan?
With the Type 2 diabetes diabetic diet in consideration, one must completely restrict from consuming packaged and processed snacks. This includes products such as cakes, bacon, cookies, chips, excess meat, cake, granola bars, coffee, and more.
Going with whole foods and edibles such as legumes, fresh fruits, green vegetables, whole grains, beans, etc. will come in handy for fighting against Type 2 diabetes. And when eating foods with high fibre content, is going to vastly reduce the level of diabetes in the body.
Conclusion
If someone seriously affected would like to reverse Type 2 diabetes, then bariatric surgery can help with the same. However, this can be the last option when all other aspects of physical exercise, diet, etc. have failed to achieve the expected results. Effective and early Type 2 diabetes treatment can help manage and cure this disease.
For the ones getting older, the healthiest way to prevent or manage Type 2 diabetes is to:
- Avoid or quit smoking.
- Eat a diabetes-friendly diet.
- Do physical exercises regularly.
And also make sure to get a monthly or yearly diabetes checkup from your nearby hospital or medical centre!
Diabetes Guides:
- You are here
- Chapter 2: 7 Best Exercise for Diabetes
- Chapter 3: Yoga for Diabetes
- Chapter 4: 6 Essential Vitamins For Diabetics
- Chapter 5: The Importance of Home Diabetes Test
- Chapter 6: What Does A Diabetic Patient Need To Be Aware Of During Covid?
- Chapter 7: 10 Diabetes Care Tips During the Coronavirus Pandemic
- Chapter 8: Diabetes Doubts




5 Comments